Bioavailability issues
Problem: Traditional supplements may have limited absorption because they break down during digestion.
Solution: Liposomal delivery
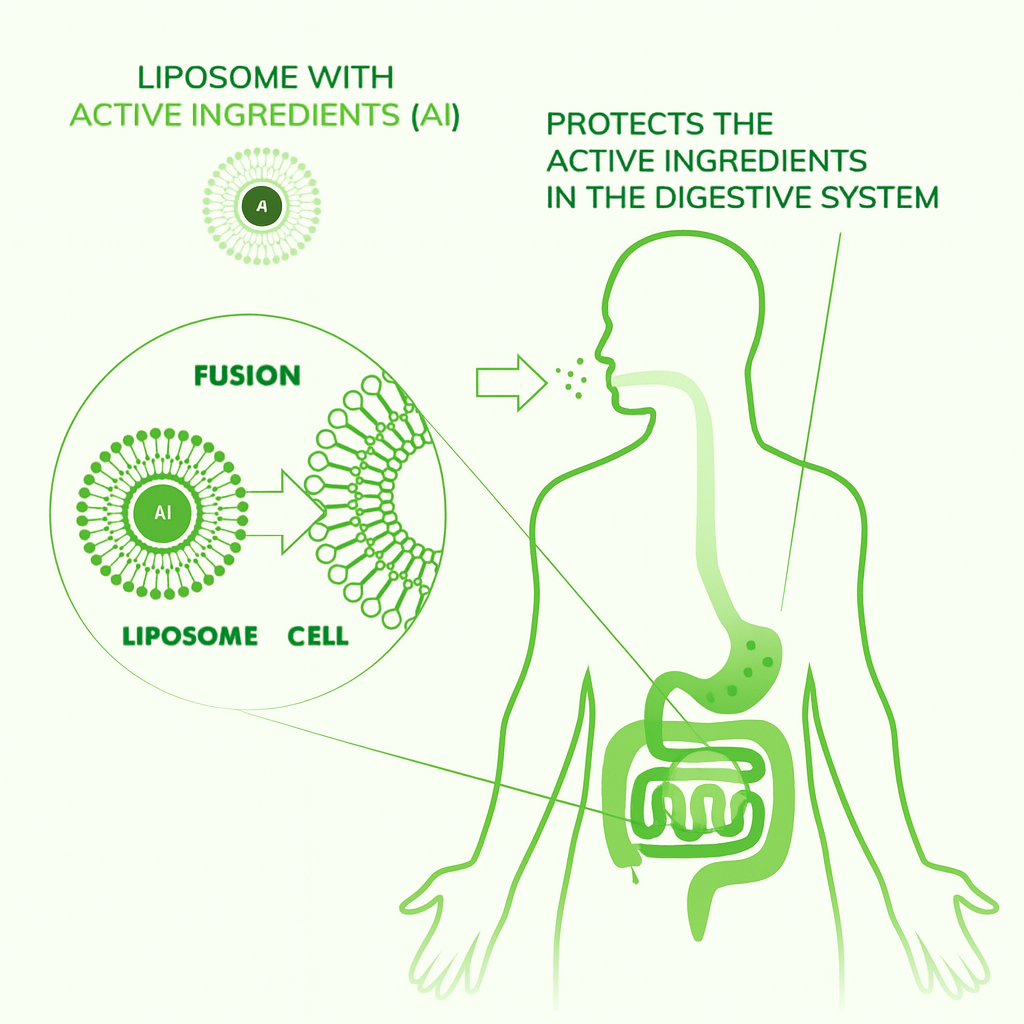
Liposomes are tiny protective spheres that help shield nutrients during digestion. This allows the nutrients to remain stable as they move through the body and helps support more efficient delivery to cells.
This delivery method helps maintain nutrient integrity and supports absorption by helping nutrients travel through the digestive environment more effectively.
Improving nutrient absorption
Supplements work best when they can be efficiently absorbed through the digestive system.
However, traditional capsules may lose some potency as they pass through the stomach and intestines.
Liposomes — made from phospholipids, the same building blocks found in cell membranes — help support more consistent nutrient delivery. Their structure allows them to merge with cells more easily, helping nutrients be utilized effectively.
Targeted Delivery
Liposomal delivery helps extend nutrient circulation time in the body, allowing for gradual release and helping support overall absorption. This method can help nutrients reach the areas where they are most useful.
Understanding the Power of Liposomes
Advanced Absorption
Liposomes can be absorbed through the oral lining and digestive pathways in a way that helps preserve their structure. This helps nutrients stay protected until they reach the bloodstream. Once inside cells, liposomes release nutrients in a form the body can use more easily.
Biocompatibility
Because liposomes are made from phospholipids similar to those found naturally in the body, they are recognized as familiar and non-irritating. This helps support comfortable digestion and efficient utilization.
Understanding the Power of Liposomes.
Liposomes can be absorbed through the oral lining and digestive pathways in a way that helps preserve their structure. This helps nutrients stay protected until they reach the bloodstream. Once inside cells, liposomes release nutrients in a form the body can use more easily.
Because liposomes are made from phospholipids similar to those found naturally in the body, they are recognized as familiar and non-irritating. This helps support comfortable digestion and efficient utilization.
Liposomes help shield nutrients by mimicking natural cell membranes. This allows nutrients to remain protected as they move through the digestive system and supports steady absorption. This method can also help make supplementation gentler for those sensitive to certain nutrients.
Liposomes are small enough to move through natural cellular pathways. This helps them deliver nutrients into cells effectively and remain available throughout the body’s circulatory and lymphatic systems.
Smaller liposomes tend to circulate more efficiently. Our Fluidizing Liposomes™ are formulated to be under 100 nm, helping support smooth movement through the body and reducing the likelihood of early breakdown.
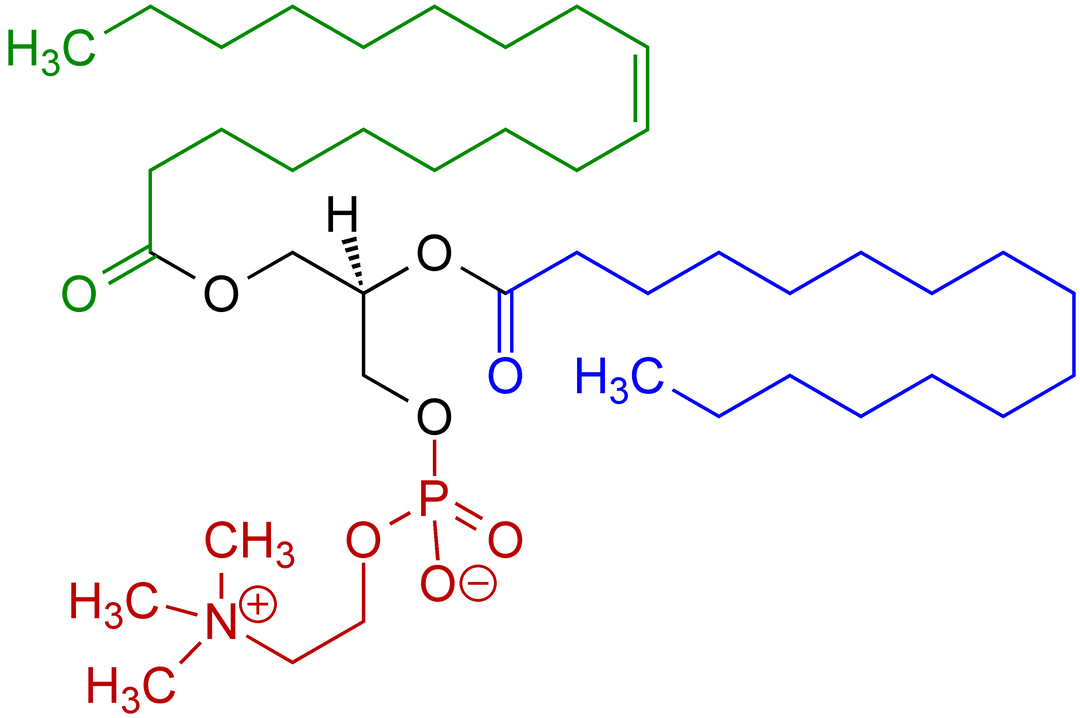
What does phosphatidylcholine do?
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) is a naturally occurring phospholipid found in many cell membranes. It plays a supportive role in normal cellular structure, communication, and overall wellness.
As natural PC levels decrease with age, some people choose to supplement it as part of their wellness routine to help support normal cellular function.

What are Liposomes made of?
Liposomes come from the Greek words lipo (fat) and soma (body). They are spherical structures formed from phosphatidylcholine — a type of phospholipid.
Liposomes can encapsulate both water-soluble and fat-soluble nutrients, helping protect them from digestion and supporting better absorption.

How do Liposomes work?
Liposomes support efficient nutrient delivery by gradually releasing nutrients after merging with cell membranes. This helps maintain nutrient stability and supports even distribution throughout the body.
Once attached to cells, liposomes can be absorbed and broken down naturally, releasing nutrients for the body to use.
Key Advantages of Liposomal Delivery
Liposomes help protect nutrients from digestion and support steady uptake.
They can carry both water-soluble and fat-soluble compounds comfortably.
Liposomal products do not typically require timing with meals.
Liposomes can carry more nutrients per particle than many traditional formats.
Their structure helps improve the amount of nutrient your body may absorb compared to standard capsules.
Liposomal formats may help maintain nutrients in the bloodstream for longer periods.








